How to Permit to Upload More Than File Html
Introduction
The ability to upload files is a central requirement for many web and mobile applications. From uploading your photo on social media to post your resume on a chore portal website, file upload is everywhere.
As a web programmer, we must know that HTML provides the support of native file upload with a bit of aid from JavaScript. With HTML5 the File API is added to the DOM. Using that, nosotros can read the FileList and the File Object within information technology. This solves multiple use-cases with files, i.east, load them locally or ship over the network to a server for processing, etc.
In this article, we volition discuss 10 such usages of HTML file upload back up. Promise you find information technology useful.
TL;DR
At any betoken in time, if you desire to play with these file upload features, you can find it from here,
- HTML File Upload Demo: https://html-file-upload.netlify.app/
The source code of the demo is in my Github repo. ✋ Feel complimentary to follow as I keep the code updated with examples. Delight requite a ⭐ if you find it useful.
- Source Code Repo: https://github.com/atapas/html-file-upload
1. Uncomplicated file upload
We can specify the input type as file to utilise the file uploader functionality in a web awarding.
<input type="file" id="file-uploader"> An input file type enables users with a push button to upload one or more files. By default, it allows uploading a unmarried file using the operating system's native file browser.
On successful upload, the File API makes it possible to read the File object using unproblematic JavaScript lawmaking. To read the File object, we need to listen to the change event of the file uploader.
Offset, get the file uploader instance by id,
const fileUploader = document.getElementById('file-uploader'); Then add a alter event listener to read the file object when the upload completes. We get the uploaded file data from the issue.target.files property.
fileUploader.addEventListener('alter', (event) => { const files = event.target.files; console.log('files', files); }); Observe the output in the browser console. Notation the FileList array with the File object having all the metadata data about the uploaded file.
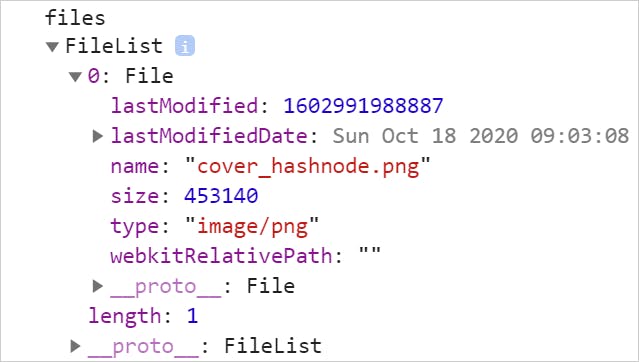
Here is the CodePen for you with the same example to explore further
two. Multiple file uploads
Nosotros tin can upload multiple files at a time. To do that, we just need to add together an attribute called, multiple to the input file tag.
<input type="file" id="file-uploader" multiple /> Now, the file browser will let you to upload one or more files to upload. Merely like the previous case, you can add a modify upshot handler to capture the information about the files uploaded. Have you noticed, the FileList is an array? Right, for multiple file uploads the array will have information equally,
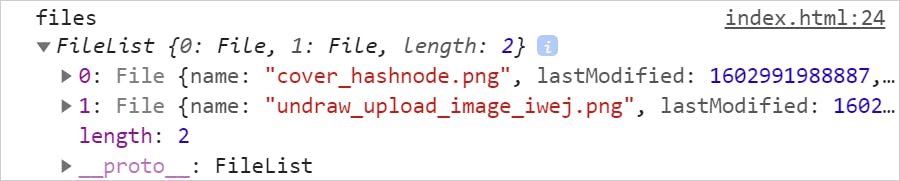
Here is the CodePen link to explore multiple file uploads.
Whenever we upload a file, the File object has the metadata data like file proper name, size, final update time, type, etc. This data tin be useful for farther validations, decision-making.
// Get the file uploader past id const fileUploader = document.getElementById('file-uploader'); // Heed to the alter event and read metadata fileUploader.addEventListener('change', (consequence) => { // Get the FileList array const files = result.target.files; // Loop through the files and get metadata for (const file of files) { const name = file.name; const type = file.type ? file.type: 'NA'; const size = file.size; const lastModified = file.lastModified; console.log({ file, name, type, size, lastModified }); } }); Hither is the output for single file upload,
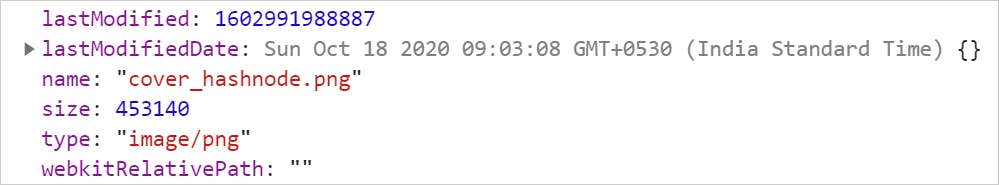
Use this CodePen to explore farther,
iv. Know well-nigh file accept property
We can utilize the accept aspect to limit the type of files to upload. You may want to testify just the allowed types of images to browse from when a user is uploading a profile picture.
<input type="file" id="file-uploader" have=".jpg, .png" multiple> In the code above, the file browser volition allow but the files with the extension jpg and png.
Note, in this case, the file browser automatically sets the file choice blazon as custom instead of all. Even so, you can e'er change it back to all files, if required.
Apply this CodePen to explore the accept attribute,
v. Manage file content
You may want to show the file content after a successful upload of information technology. For profile pictures, information technology will be disruptive if we exercise not prove the uploaded film to the user immediately after upload.
We tin can employ the FileReader object to convert the file to a binary string. Then add together a load event listener to get the binary string on successful file upload.
// Get the instance of the FileReader const reader = new FileReader(); fileUploader.addEventListener('change', (event) => { const files = outcome.target.files; const file = files[0]; // Get the file object after upload and read the // data as URL binary string reader.readAsDataURL(file); // One time loaded, practice something with the string reader.addEventListener('load', (consequence) => { // Hither nosotros are creating an epitome tag and adding // an paradigm to it. const img = document.createElement('img'); imageGrid.appendChild(img); img.src = issue.target.event; img.alt = file.proper name; }); }); Try selecting an image file in the CodePen below and see it renders.
6. Validate file size
As we have seen, we can read the size metadata of a file, we can really employ it for a file size validation. Yous may let users to upload an epitome file up to 1MB. Allow united states of america meet how to achieve that.
// Listener for file upload change event fileUploader.addEventListener('change', (event) => { // Read the file size const file = event.target.files[0]; const size = file.size; let msg = ''; // Bank check if the file size is bigger than 1MB and ready a message. if (size > 1024 * 1024) { msg = `<span manner="color:red;">The allowed file size is 1MB. The file you lot are trying to upload is of ${returnFileSize(size)}</span>`; } else { msg = `<span mode="color:green;"> A ${returnFileSize(size)} file has been uploaded successfully. </span>`; } // Show the bulletin to the user feedback.innerHTML = msg; }); Try uploading a file of dissimilar sizes to see how the validation works,
seven. Evidence file upload progress
The meliorate usability is to let your users know most a file upload progress. We are now enlightened of the FileReader and the event to read and load the file.
const reader = new FileReader(); The FileReader has some other event called, progress to know how much has been loaded. We tin can employ HTML5'southward progress tag to create a progress bar with this information.
reader.addEventListener('progress', (event) => { if (upshot.loaded && issue.total) { // Calculate the pct completed const percent = (consequence.loaded / result.total) * 100; // Set the value to the progress component progress.value = percent; } }); How nearly you effort uploading a bigger file and see the progress bar working in the CodePen below? Requite information technology a try.
8. How about directory upload?
Can we upload an unabridged directory? Well, it is possible merely with some limitations. There is a non-standard aspect(at least, while writing this article) called, webkitdirectory that allows united states of america to upload an unabridged directory.
Though originally implemented only for WebKit-based browsers, webkitdirectory is also usable in Microsoft Edge as well as Firefox 50 and subsequently. However, fifty-fifty though it has relatively wide back up, it is still non standard and should not exist used unless you have no alternative.
You can specify this attribute as,
<input type="file" id="file-uploader" webkitdirectory /> This will allow you lot to select a binder(aka, directory),
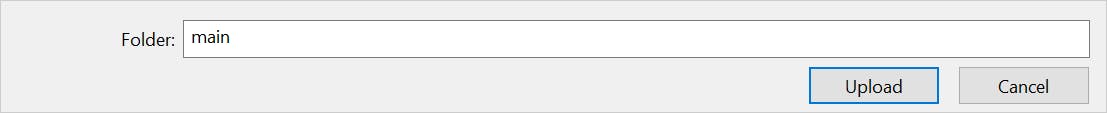
User has to provide a confirmation to upload a directory,
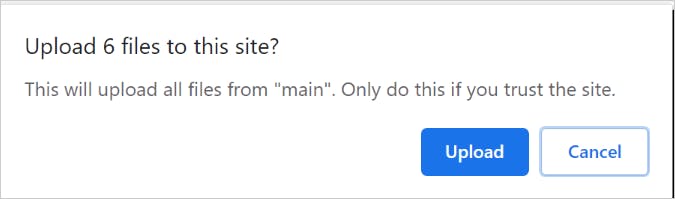
Once the user clicks the Upload button, the uploading takes place. 1 important point to notation here. The FileList array volition have data most all the files in the uploaded directory every bit a flat structure. But the central is, for each of the File objects, the webkitRelativePath attribute will have the directory path.
For example, let united states consider a main directory and other folders and files under information technology,
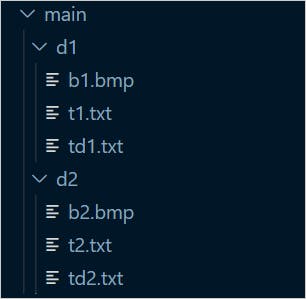
Now the File objects will have the webkitRelativePath populated as,
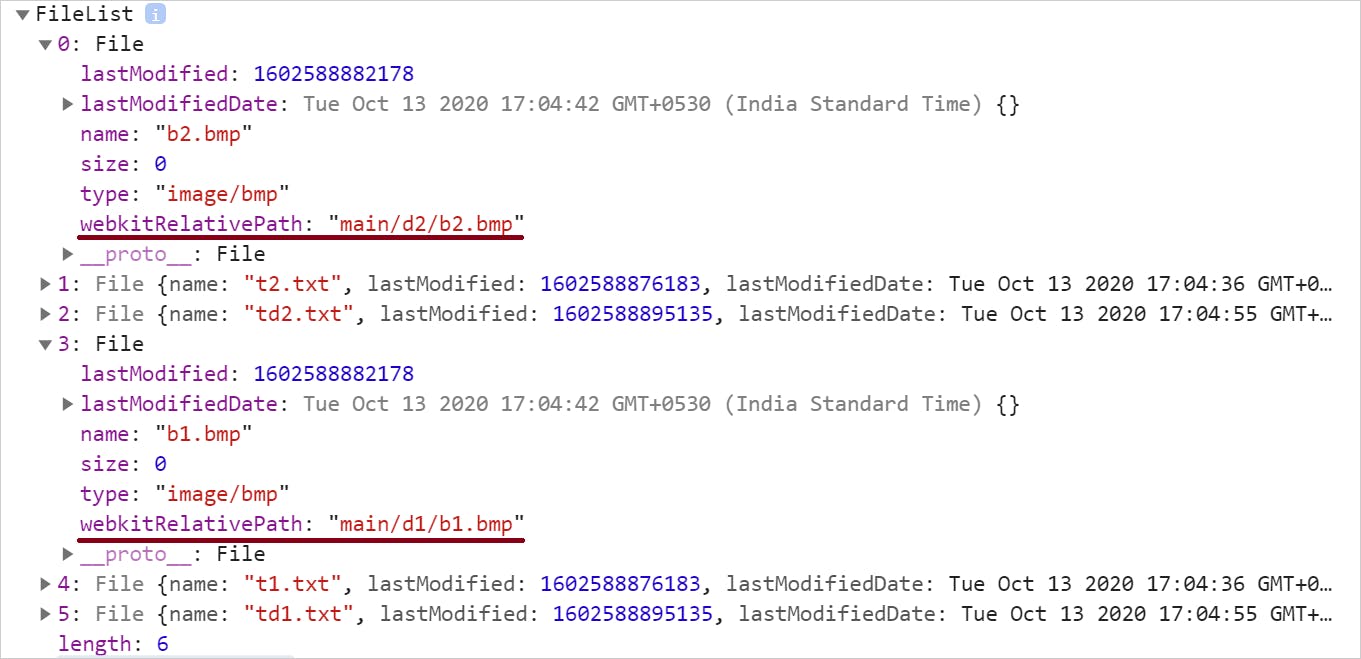
Yous can use it to render the folder and files in whatever UI construction of your choice. Use this CodePen to explore further.
9. Allow'due south drag, drop and upload
Not supporting a drag-and-driblet for file upload is kinda old fashion, isn't it? Let us see how to achieve that with a few simple steps.
Kickoff, create a drop zone and optionally a section to prove the uploaded file content. We volition use an paradigm as a file to drag and drop here.
<div id="container"> <h1>Drag & Drop an Epitome</h1> <div id="drib-zone"> Driblet HERE </div> <div id="content"> Your image to appear here.. </div> </div> Get the dropzone and the content areas past their respective ids.
const dropZone = document.getElementById('driblet-zone'); const content = certificate.getElementById('content'); Add together a dragover upshot handler to show the effect of something going to be copied,
dropZone.addEventListener('dragover', event => { event.stopPropagation(); outcome.preventDefault(); upshot.dataTransfer.dropEffect = 'copy'; }); 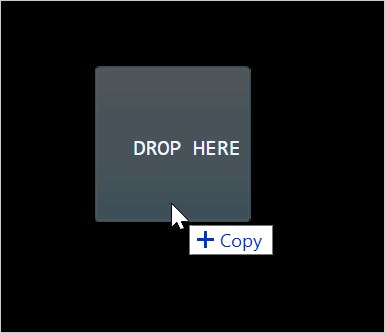
Next, define what we want to do when the prototype is dropped. We will demand a driblet issue listener to handle that.
dropZone.addEventListener('drop', event => { // Become the files const files = upshot.dataTransfer.files; // At present we can do everything possible to show the // file content in an HTML chemical element similar, DIV }); Try to drag and drop an image file in the CodePen example below and see how it works. Practise not forget to see the code to return the dropped image as well.
ten. Handle files with objectURLs
In that location is a special method called, URL.createObjectURL() to create an unique URL from the file. You lot can also release it past using URL.revokeObjectURL() method.
The DOM
URL.createObjectURL()andURL.revokeObjectURL()methods let yous create simple URL strings that can be used to reference any data that can be referred to using a DOM File object, including local files on the user'southward estimator.
A elementary usage of the object URL is,
img.src = URL.createObjectURL(file); Employ this CodePen to explore the object URL further. Hint: Compare this approach with the arroyo mentioned in #v previously.
Determination
I truly believe this,
Many times a native HTML characteristic may be enough for us to bargain with the use-cases in hands. I found, file upload is 1 such that provides many cool options by default.
Let me know if this article was useful to you by commenting below. You may also like,
- 10 useful HTML5 features, you lot may not exist using
- I made a photo gallery with CSS animation. Here'southward what I learned.
- 10 lesser-known Spider web APIs you may want to use
If information technology was useful to you, please Similar/Share and then that, it reaches others as well. Please hit the Subscribe push at the top of the page to get an electronic mail notification on my latest posts.
You can @ me on Twitter (@tapasadhikary) with comments, or feel costless to follow me.
Source: https://blog.greenroots.info/10-useful-html-file-upload-tips-for-web-developers
0 Response to "How to Permit to Upload More Than File Html"
Post a Comment